We all know that the conventional Air conditioning consumes lot of electricity which in turn releases millions of tons of carbon di oxide, a green house gas which is known to be harmful to environment. The green house gas emissions have increased by 25% in the last 150 years since the industrial revolution.
The demand for air conditioning is growing as the temperatures are increasing. Heat waves cause health problems and some times even death too. There was news in year 2003 that around 35,000 people died in Europe from a heat wave. So the demand for air conditioning units is increasing day by day. But using the conventional electricity lot of green house gases are being released into atmosphere.
It is the time now to put a brake to the effects of climate changes by replacing conventional energy with renewable and natural energy like Solar Power. The only option till now for reducing the energy consumed by air conditioners is to simply turn them off. But the Solar Air Conditioners take the advantage of the sun shine and use that energy to cool you during the hottest part of the day. Let us see how a solar air conditioner works.. Let us first know about how a conventional air conditioner works and then go to solar air conditioner.
 You may be knowing that the compressor in your air conditioner is used for raising the temperature of the refrigerant fluid which is necessary to produce cool air. The idea is to use Solar Energy to raise this temperature and reduce the compressor's work load and allow the compressor to consume less energy. Let us see how a conventional air conditioner works and then go to solar air conditioners.
You may be knowing that the compressor in your air conditioner is used for raising the temperature of the refrigerant fluid which is necessary to produce cool air. The idea is to use Solar Energy to raise this temperature and reduce the compressor's work load and allow the compressor to consume less energy. Let us see how a conventional air conditioner works and then go to solar air conditioners.
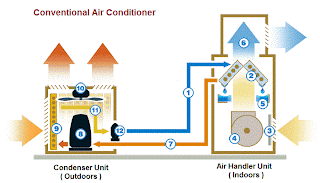
The Refrigerators and Air Conditioners use a fluid called refrigerant to produce cool air. The refrigerant works like a sponge, soaking up the heat from indoor air and then transporting it to outside where the heat is squeezed out of the sponge into the air. The refrigerant flowing through a coil - a series of metal tubes - inside the air conditioner's air handler is very cold ( -6 to +4 degrees celcius). We all know that heat always flows from hotter place to cooler place. So if the indoor air at 37 deg. celcius is blowing through the air handler, heat will be removed from the air and absorbed by the refrigerant which is much cooler. So the temperature of the air reduces as heat is removed. So the air leaving the air handler is much cooler than the room temperature.
The metal coil inside the air handler is called as evaporator. The heat absorbed by refrigerant causes it to evaporate and turn it into gas. Here comes the actual problem. We know that heat always flows from a hotter place to cooler place. We want to send the heat absorbed by refrigerant into outside air but if the refrigerant gas is at temperature of say +12 deg celcius, and outside air is at +26 to +40 deg celcius, this won't work. We need to find out some way to increase the refrigerant gas temperature to be higher than outside temperature so that the heat absorbed by refrigerant can be dumped to outside.
We know that by compressing a gas increase its pressure which also increases its temperature. So the job of a compressor in an Air Conditioner is to compress the refrigerant gas coming from the evaporator coil so that its temperature is raised from 12 deg to 75 deg celcius or more. With the temperature of refrigerant more than outside temperature, the heat stored in refrigerant is transferred to outside air.
So how the Solar Energy helps
 We know that in order to keep the room cooler, the hot refrigerant gas has to be released to outside air and its temperature has to be higher than outside air in order this to happen. We can send the refrigerant through a solar energy collector before it reaches the compressor, and the solar energy can do a portion of the work of the compressor - heating of the refrigerant. This allows the compressor to run less and consume less electricity or to operate at lower speed and thus save electricity. Please see the diagram given here to know about this process.
We know that in order to keep the room cooler, the hot refrigerant gas has to be released to outside air and its temperature has to be higher than outside air in order this to happen. We can send the refrigerant through a solar energy collector before it reaches the compressor, and the solar energy can do a portion of the work of the compressor - heating of the refrigerant. This allows the compressor to run less and consume less electricity or to operate at lower speed and thus save electricity. Please see the diagram given here to know about this process.
The refrigerant cools while moving through the condenser coil to around 29-43 deg celcius. Another trick is used to get the refrigerant back to -6 to +4 deg celcius which is necessary for cooling. As compressing increases the temperature of refrigerant, we expand it to reduce the temperature. This is done by forcing the refrigerant through a tiny opening - called as an expansion valve - which allows the refrigerant's pressure and temperature to fall drastically as it comes out from the tiny passage.
When the refrigerant cools back to -6 to +4 deg celcius, the cycle repeats.
The demand for air conditioning is growing as the temperatures are increasing. Heat waves cause health problems and some times even death too. There was news in year 2003 that around 35,000 people died in Europe from a heat wave. So the demand for air conditioning units is increasing day by day. But using the conventional electricity lot of green house gases are being released into atmosphere.
It is the time now to put a brake to the effects of climate changes by replacing conventional energy with renewable and natural energy like Solar Power. The only option till now for reducing the energy consumed by air conditioners is to simply turn them off. But the Solar Air Conditioners take the advantage of the sun shine and use that energy to cool you during the hottest part of the day. Let us see how a solar air conditioner works.. Let us first know about how a conventional air conditioner works and then go to solar air conditioner.
How a conventional Air Conditioner works?
 You may be knowing that the compressor in your air conditioner is used for raising the temperature of the refrigerant fluid which is necessary to produce cool air. The idea is to use Solar Energy to raise this temperature and reduce the compressor's work load and allow the compressor to consume less energy. Let us see how a conventional air conditioner works and then go to solar air conditioners.
You may be knowing that the compressor in your air conditioner is used for raising the temperature of the refrigerant fluid which is necessary to produce cool air. The idea is to use Solar Energy to raise this temperature and reduce the compressor's work load and allow the compressor to consume less energy. Let us see how a conventional air conditioner works and then go to solar air conditioners.The Refrigerators and Air Conditioners use a fluid called refrigerant to produce cool air. The refrigerant works like a sponge, soaking up the heat from indoor air and then transporting it to outside where the heat is squeezed out of the sponge into the air. The refrigerant flowing through a coil - a series of metal tubes - inside the air conditioner's air handler is very cold ( -6 to +4 degrees celcius). We all know that heat always flows from hotter place to cooler place. So if the indoor air at 37 deg. celcius is blowing through the air handler, heat will be removed from the air and absorbed by the refrigerant which is much cooler. So the temperature of the air reduces as heat is removed. So the air leaving the air handler is much cooler than the room temperature.
The metal coil inside the air handler is called as evaporator. The heat absorbed by refrigerant causes it to evaporate and turn it into gas. Here comes the actual problem. We know that heat always flows from a hotter place to cooler place. We want to send the heat absorbed by refrigerant into outside air but if the refrigerant gas is at temperature of say +12 deg celcius, and outside air is at +26 to +40 deg celcius, this won't work. We need to find out some way to increase the refrigerant gas temperature to be higher than outside temperature so that the heat absorbed by refrigerant can be dumped to outside.
We know that by compressing a gas increase its pressure which also increases its temperature. So the job of a compressor in an Air Conditioner is to compress the refrigerant gas coming from the evaporator coil so that its temperature is raised from 12 deg to 75 deg celcius or more. With the temperature of refrigerant more than outside temperature, the heat stored in refrigerant is transferred to outside air.
So how the Solar Energy helps
 We know that in order to keep the room cooler, the hot refrigerant gas has to be released to outside air and its temperature has to be higher than outside air in order this to happen. We can send the refrigerant through a solar energy collector before it reaches the compressor, and the solar energy can do a portion of the work of the compressor - heating of the refrigerant. This allows the compressor to run less and consume less electricity or to operate at lower speed and thus save electricity. Please see the diagram given here to know about this process.
We know that in order to keep the room cooler, the hot refrigerant gas has to be released to outside air and its temperature has to be higher than outside air in order this to happen. We can send the refrigerant through a solar energy collector before it reaches the compressor, and the solar energy can do a portion of the work of the compressor - heating of the refrigerant. This allows the compressor to run less and consume less electricity or to operate at lower speed and thus save electricity. Please see the diagram given here to know about this process.How the heat is dumped outside?
The hot refrigerant gas which leaves compressor flows into another coil called as the condenser coil. This coil is similar to car radiator, radiating heat from the hot refrigerant into the outside atmosphere as one fan pulls outside air across the coil. It is called as condenser coil because the refrigerant gas condenses back into liquid form as the heat is given to outside air.The refrigerant cools while moving through the condenser coil to around 29-43 deg celcius. Another trick is used to get the refrigerant back to -6 to +4 deg celcius which is necessary for cooling. As compressing increases the temperature of refrigerant, we expand it to reduce the temperature. This is done by forcing the refrigerant through a tiny opening - called as an expansion valve - which allows the refrigerant's pressure and temperature to fall drastically as it comes out from the tiny passage.
When the refrigerant cools back to -6 to +4 deg celcius, the cycle repeats.
No comments:
Post a Comment